Sustainable urban landscapes: Computer-aided sustainability evaluation for landscape design
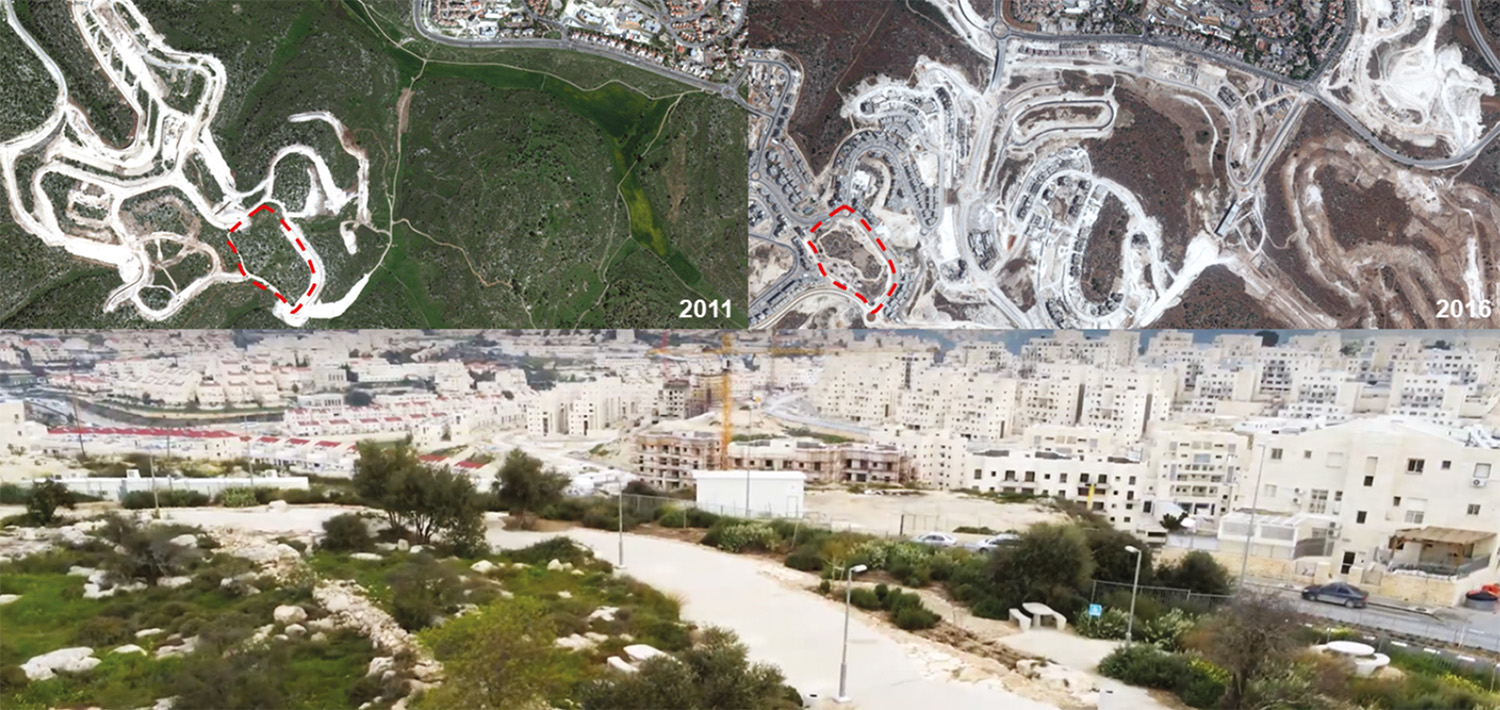
Measuring socio-ecological indicators in early design models is essential for advancing sustainability designs and a stepping-stone towards the broad integration of high-performance urban development solutions. Sustainability Rating Systems are standard methods for achieving sustainable development of buildings and urban landscapes. However, they suffer from low adoption and implementation rates due to labour-intensive evaluation processes.
Recent advancements in computational dataset availability and coding assimilation call for a re-evaluation ofsustainability design practices in the urban-landscape realm.
This study explores how recent advancements in big data, combined with the availability of new urban environment datasets, could advance sustainability rating systems in landscape development. It contributes to urban landscape sustainability by suggesting a computation evaluation method and tool for early design stages. The study compares existing computational technology (supply) and industry performance evaluation needs (demand) using a systematic review and survey of professional communities as a case study.
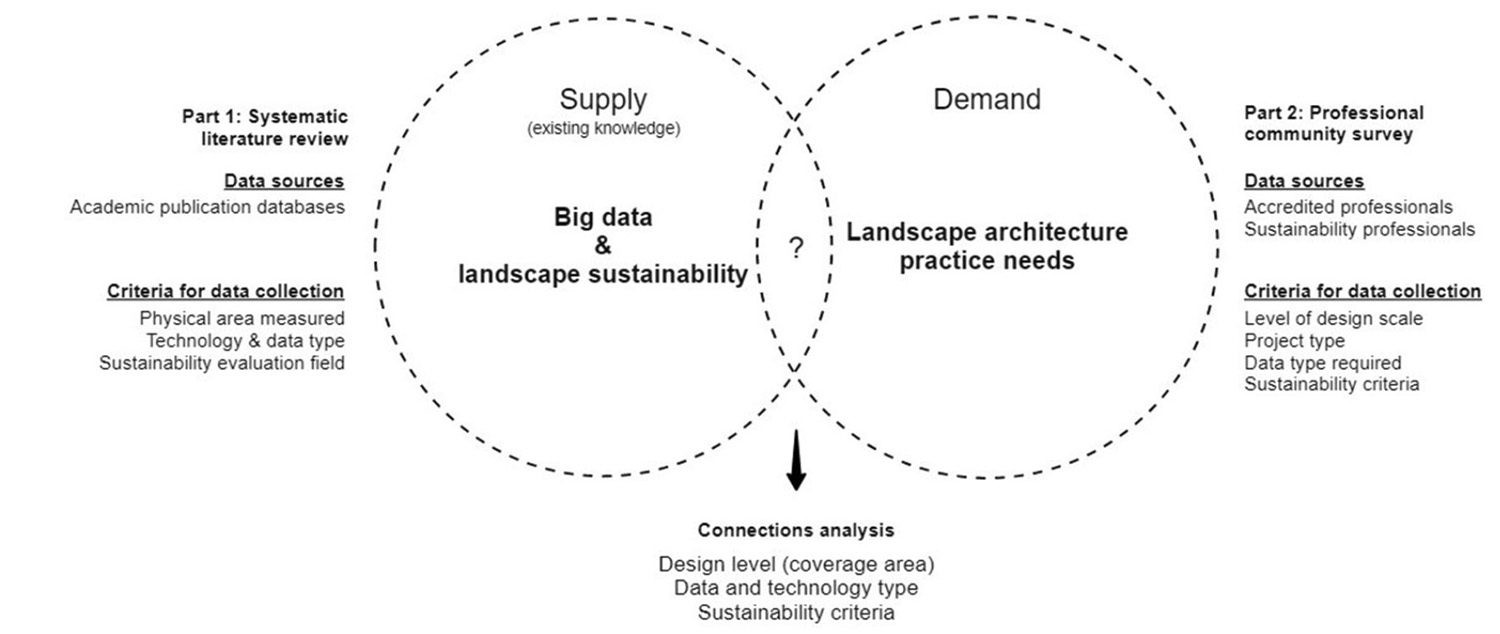
Based on the comparison results, it develops a methodological framework for employing computer-aided design to evaluate potential measurement methods for sustainability performance in urban-landscape developments.
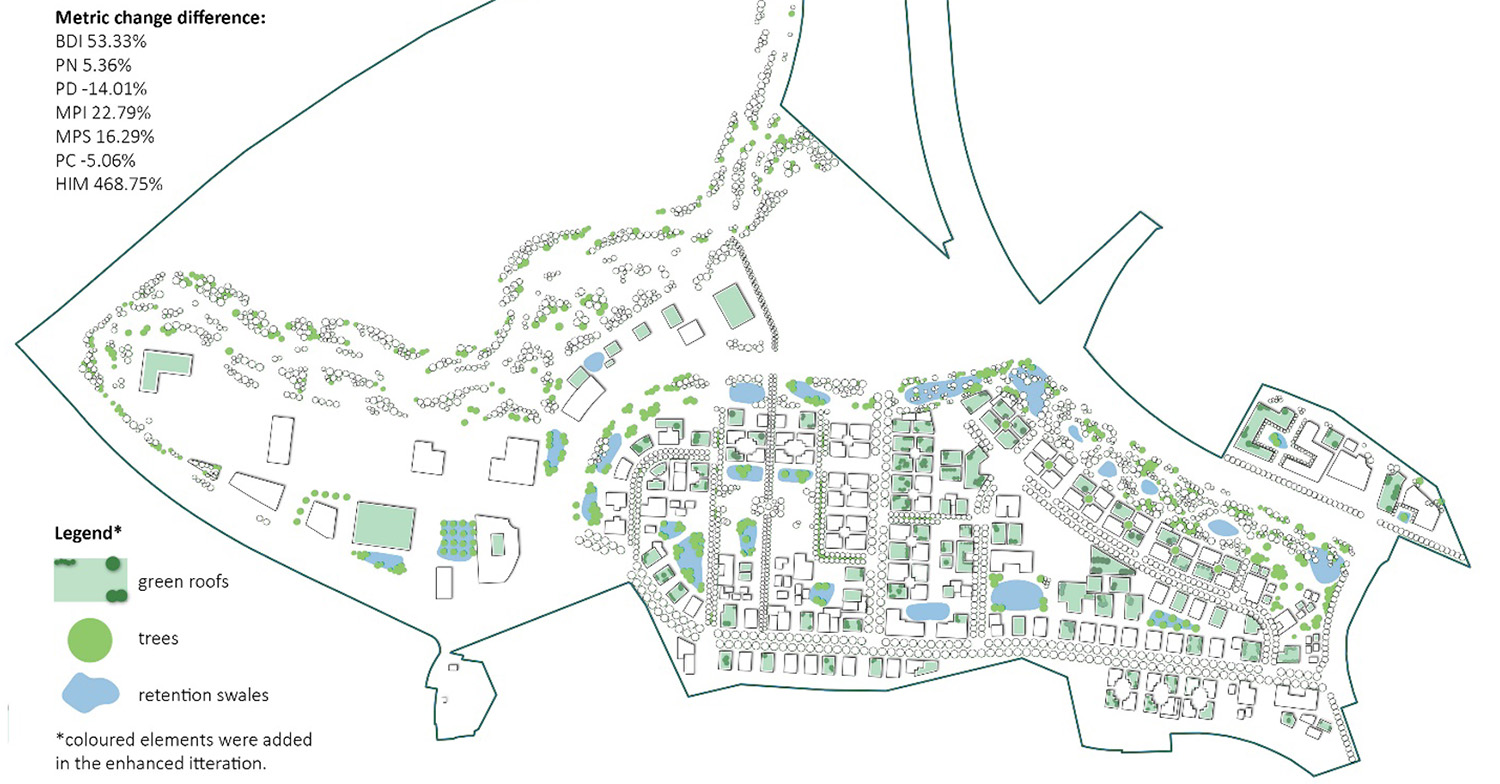
The method analyses and visualizes the selected design's performance criteria directly on the computation model, thus informing the designer about the sustainability performance early in the development phase. The method and tool significantly improve the design's performance in vegetation biomass optimization, urban heat mitigation, and precipitation management. The computation model also provided ecological spatial metrics important for sustainability benchmarking level. Our review revealed that this level also holds available big data sustainability evaluation methods and technologies.
Specifically, directed data for measuring ecology and volunteered and automated data for measuring social indicators. Such supply-demand links could significantly advance evaluation methods toward achieving a broader application of sustainable urban development.
Collaboration:
The project is performed in collaboration with prof. Pnina Plaut
Scientific publications that were published on this research:
Yoffe, H. Plaut, P. Grobman, Y.J. Towards sustainability evaluation of urban landscapes using big data: a case study of Israel's architecture, engineering and construction industry. Landscape Research 47(1). 49-67. 2022. DOI: 10.1080/01426397.2021.1970123.