Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in landscape and architectural design
Although Sustainable design of buildings is considered a standard practice in the architectural engineering and construction (AEC) industry, sustainable design of neighborhoods is still considered a labor-intensive, expert-dependent, and time-demanding process with low implementation rates. Recent technological advancements in Building information modeling (BIM) and Geo-design, together with the abundance of sensorial and photo information on the built environment, promote automation, analysis, and visualization of sustainability performance in design. Integration of automation using machine learning (ML) methods that provide access to previously tedious tasks can help reduce calculation and evaluation time. It can also improve decision-making, minimize human error, and shorten process planning times.
The research is conducted in two parallel directions:
- Theoretical research - examining the potential of AI to contribute to the building industry in general and specifically in Israel.
- Practical research - developing tools for architecture and landscape urban design
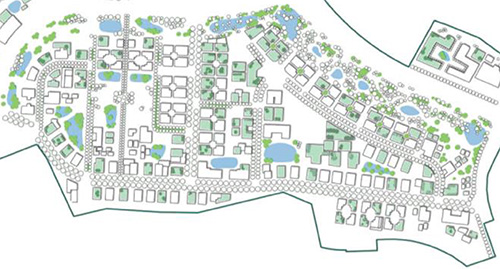
Two practical directions are currently developed. The first focuses on landscape design. In urban landscape design, ML methods were used for tasks such as the classification of buildings, land use and roof types, quality evaluation of building facades, visual quality of streets, and citizens' perception of the built environment, such as safety aspects, in growing numbers each year.
Although significant work has been undertaken in this area, there seems to be less focus on evaluating urban landscapes at the neighborhood level, specifically regarding sustainability aspects: design's social, ecological, and resiliency. Furthermore, to our knowledge, none of the automation processes found in the existing literature uses expert-based evaluation datasets.
This direction aims to advance computational sustainability by introducing a framework for sustainability evaluation using expert-based knowledge and machine learning. It also suggests a preliminary method that uses a convolutional neural network algorithm trained to evaluate the sustainability properties of plans based on expert-evaluation data collection.
The second direction develops a ML-based data collection and analysis method for urban-architectural information based on Earth Observation (EO) data. The model will analyze the EO data and generate new knowledge that will allow decision-makers a much broader range of urban-architectural information on features such as building typology, residential density, height, size, and use.
Funding:
Machine Learning for improving permitting processes in Israel: Feasibility, Benefits, Potentials, and Blockers. Principal investigator together with Dr. Guy Austern. Israeli Ministry of Construction and Housing. 261,000NIS (~78,000US$). 2022
Collaboration:
The project is performed in collaboration with Dr. Guy Austern
Scientific publications that were published on this research:
Raanan N., Yoffe H., Zeev, G., Plaut P., Grobman, Y.J., “Machine Learning Tool for Sustainability Evaluation: The Case of Neighborhoods”. Jeroen van Ameijde, Nicole Gardner, Kyung Hoon Hyun, Dan Luo, Urvi Sheth (eds.), POST-CARBON. Proceedings of the 27th CAADRIA Conference, Sydney, 9-15 April 2022, pp. 283-291